果然还是对概率期望不感冒。。。
还是种田很酷很炫的算法适合老子。
前言
又一个学长要讲而我还不会的算法。
对一棵树进行操作,而其中的关键点并不多,且非关键点是无关紧要的,就可以上虚树($Virtual\ Tree$),用$O$(关键点数)的时间搞事情了。
抄袭来源
虚树
实现
有一个$O(n)$的$DP$:
设$f(i)$为阻断点$i$到其子树所有关键点最小代价。
记$x$为$i$的某个儿子,若$x$为关键点,有$len(edge(i,x))$的贡献;否则有$\min\{len(edge(i,x)),f(x)\}$的贡献。答案为$f(1)$。
如果构造出虚树在虚树上$DP$,复杂度就是对的了。
虚树保留了关键点和它们两两之间的$lca$,就是酱紫(红色的为关键点):
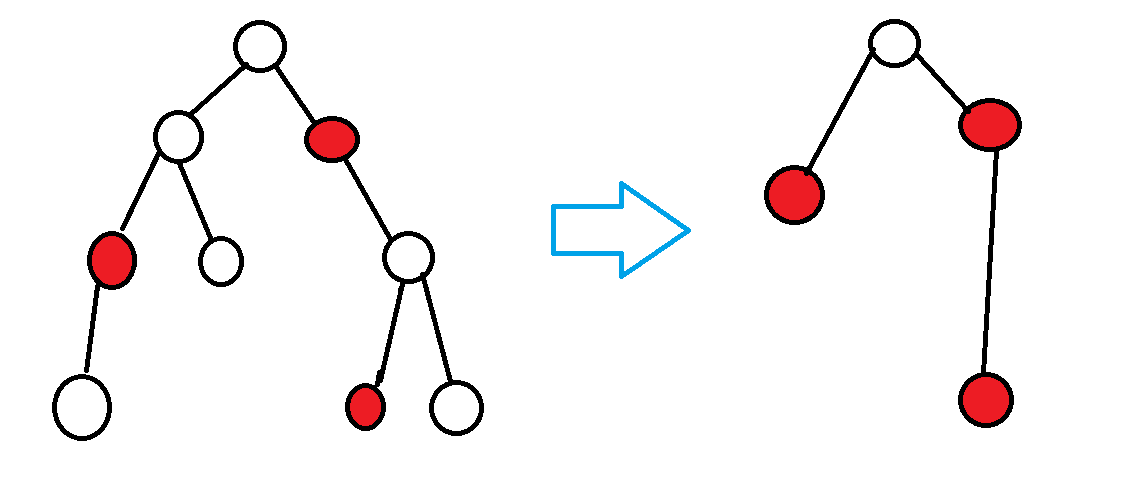
在栗子中,压缩进去的链以边权为其最小值的边代替。
虚树构造的核心是用单调栈维护虚树的一条链,单调栈从上至下$dfs$序递减,某个节点的爹是它在栈中下面的点。
对关键点按$dfs$序排序,先把点$1$加进去,再依次把每个关键点加进去:
求出它与栈顶的$lca$记为$l$。
若栈顶为$l$,说明新加的点挂在这条链下面,直接压进栈里。
(红色为当前的链,蓝色为新加的点)
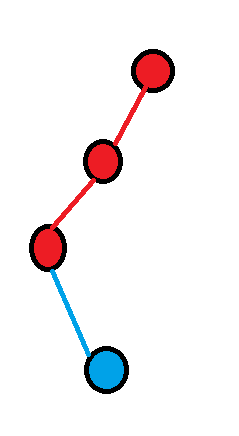
若栈顶不为$l$,维护的链就会变为根节点到新点的链,栈中弹出$dfs$序比$l$大的点,并把弹出的点与它爹(它下面的点)连边。
这时可能$l$不在链上(下图右),需要额外加进去。
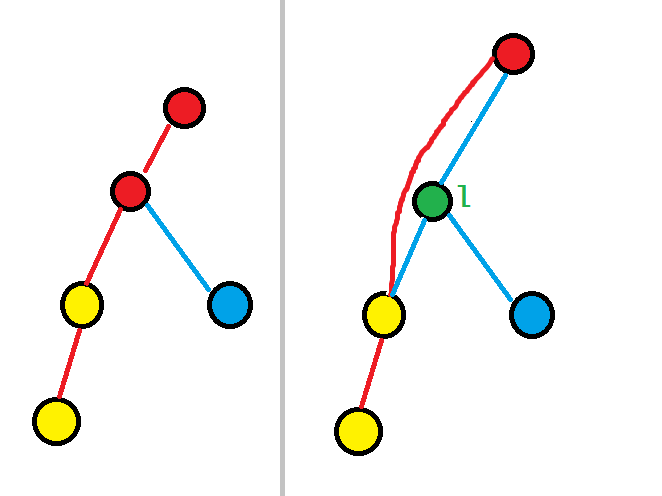
所有关键点处理完后,把栈中剩余的点之间连边。
代码
细节很多。。。
int h[maxn],seg[maxn],num,n;//seg为dfs序,n为关键点数
vector<int>p;//p存储关键点
struct edge{
int pre,to,l;
}e[maxn<<1];
inline bool cmp(int x,int y){return seg[x]<seg[y];}
inline void add(int from,int to){
int l=query(from,to);//query是查询两点间最小值
e[++num].pre=h[from],h[from]=num,e[num].to=to,e[num].l=l;
e[++num].pre=h[to],h[to]=num,e[num].to=from,e[num].l=l;
}
struct Monostack{
int sta[maxn],top;
void clear(){
for(register int i=2;i<=top;++i)add(sta[i],sta[i-1]);
top=0;
}
void push(int x){
sta[++top]=x;
}
void check(int x){
int l=lca(sta[top],x);
h[x]=0;
if(l!=sta[top]){
while(seg[l]<seg[sta[top-1]])add(sta[top],sta[top-1]),--top;
--top;
if(l==sta[top])add(l,sta[top+1]);
else h[l]=0,add(l,sta[top+1]),push(l);
}
push(x);
}
}s;//单调栈
void build(){
h[1]=0,s.push(1);
sort(p.begin(),p.end(),cmp);//以dfs序排序
for(vector<int>::iterator iter=p.begin();iter!=p.end();++iter)s.check(*iter);
s.clear();
}
每个点入栈时清空邻接表头指针,防止大量$memset$耗费时间
栗子完整代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#define maxn 250005
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
inline int read(){
int x=0,y=0;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')y=1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9')x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch^48),ch=getchar();
return y?-x:x;
}
namespace origin{
int h[maxn],seg[maxn],fa[maxn],deep[maxn],top[maxn],siz[maxn],son[maxn],f[maxn][22],lg[maxn],a[maxn],all,num,n;
struct edge{
int pre,to,l;
}e[maxn<<1];
inline void add(int from,int to,int l){
e[++num].pre=h[from],h[from]=num,e[num].to=to,e[num].l=l;
}
void dfs1(int node=1){
siz[node]=1;
int x;
for(register int i=h[node];i;i=e[i].pre){
x=e[i].to;
if(!siz[x]){
a[x]=e[i].l,fa[x]=node,deep[x]=deep[node]+1,dfs1(x),siz[node]+=siz[x];
if(siz[x]>siz[son[node]])son[node]=x;
}
}
}
void dfs2(int node=1){
f[seg[node]=++all][0]=a[node];
if(son[node]){
top[son[node]]=top[node],dfs2(son[node]);
int x;
for(register int i=h[node];i;i=e[i].pre){
x=e[i].to;
if(!seg[x])top[x]=x,dfs2(x);
}
}
}
inline int lca(int x,int y){
while(top[x]!=top[y])deep[top[x]]<deep[top[y]]?y=fa[top[y]]:x=fa[top[x]];
return deep[x]<deep[y]?x:y;
}
void ST(){
for(register int i=2;i<=n;++i)lg[i]=lg[i>>1]+1;
for(register int j=1;j<=lg[n];++j)
for(register int i=1;i+(1<<j)-1<=n;++i)
f[i][j]=min(f[i][j-1],f[i+(1<<j-1)][j-1]);
}
inline void init(){
dfs1(),dfs2(),ST();
}
inline int ask(int l,int r){
int len=lg[r-l+1];
return min(f[l][len],f[r-(1<<len)+1][len]);
}
int query(int x,int y){
int ans=inf;
while(top[x]!=top[y]){
if(deep[top[x]]<deep[top[y]])swap(x,y);
ans=min(ans,ask(seg[top[x]],seg[x]));
x=fa[top[x]];
}
if(x==y)return ans;
if(deep[x]<deep[y])swap(x,y);
return min(ans,ask(seg[y]+1,seg[x]));
}
}
namespace virt{
int h[maxn],num,n;
long long f[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
vector<int>p;
struct edge{
int pre,to,l;
}e[maxn<<1];
inline void add(int from,int to){
int l=origin::query(from,to);
e[++num].pre=h[from],h[from]=num,e[num].to=to,e[num].l=l;
e[++num].pre=h[to],h[to]=num,e[num].to=from,e[num].l=l;
}
struct Monostack{
int sta[maxn],top;
void clear(){
for(register int i=2;i<=top;++i)add(sta[i],sta[i-1]);
top=0;
}
void push(int x){
sta[++top]=x;
}
void check(int x){
h[x]=0;
int l=origin::lca(sta[top],x);
if(l!=sta[top]){
while(origin::seg[l]<origin::seg[sta[top-1]])add(sta[top],sta[top-1]),--top;
--top;
if(l!=sta[top])h[l]=0,add(sta[top+1],l),push(l);
else add(sta[top+1],l);
}
push(x);
}
}s;
inline bool cmp(int x,int y){return origin::seg[x]<origin::seg[y];}
void build(){
h[1]=0,s.push(1);
for(vector<int>::iterator iter=p.begin();iter!=p.end();++iter)s.check(*iter);
s.clear();
}
void dp(int node=1,int fa=0){
f[node]=0;
int x;
for(register int i=h[node];i;i=e[i].pre){
x=e[i].to;
if(x!=fa){
if(vis[x])f[node]+=e[i].l;
else dp(x,node),f[node]+=min(1ll*e[i].l,f[x]);
}
}
}
void solve(){
num=0,p.clear(),n=read();
int x;
for(register int i=1;i<=n;++i)p.push_back(x=read()),vis[x]=1;
sort(p.begin(),p.end(),cmp);
build(),dp();
printf("%lld\n",f[1]);
for(vector<int>::iterator iter=p.begin();iter!=p.end();++iter)vis[*iter]=0;
}
}
int main(){
origin::n=read();
int x,y,z,t;
for(register int i=1;i<origin::n;++i)x=read(),y=read(),z=read(),origin::add(x,y,z),origin::add(y,x,z);
origin::init();
t=read();
while(t--)virt::solve();
}
复杂度
$n$个关键点的虚树点数不超过$2n-1$,感觉是比较显然的吧。。。
栗子中用树剖+ST表求链最小值,树剖求$lca$,复杂度为$O(\sum k\log n)$。
从代码里也能看出整个虚树构造是$O(k\log n)$的,若用$O(1)LCA$的话还是带一个排序的$\log k$。
水题
大工程
Kingdom and its Cities
世界树
Surprise me!
莫比乌斯反演+虚树。
SvT
$SAM$+虚树。







